Pneumonia
- An infection that inflames air sacs in one or both lungs which may fill with fluid or pus.
TYPES OF PNEUMONIA
according to Clinical classification
Lobar pneumonia:
All or large segment of pulmonary lobe is involved
Bronchopneumonia:
Begins in terminal bronchioles and scattered in air spaces throughout the lungs.
Interstitial pneumonia:
Affects alveolar walls (Interstitium)
TYPES OF PNEUMONIA
- Community acquired pneumonia (CAP)
- Hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP)
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)
- Health care associated pneumonia (HCAP)
- Aspiration pneumonia
Microorganism that cause pneumonia
Bacteria:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Viruses:
- Rhinoviruses, Coronaviruses, Influenza, RSV
Fungi:
- Pneumocystis jeroveci, Aspergillus, Candida
Parasites:
- Toxoplasma gondii, Stercoralis and others.
Risk factors of Pneumonia
- Age: 65 or older and less than 2
- Smokers
- Recent respiratory infection
- Chronic lung diseases COPD
- Chronic illness heart disease, diabetes
- Weak immune system
- Difficulty swallowing like stroke, neurological condition
- Long time Hospitalization
Sign and symptoms of Pneumonia
- Chest Pain (while breathing or coughing)
- Cough with phlegm or mucus
- Bacterial pneumonia: green/yellow mucus
- Atypical pneumonia: white mucus
- Virus pneumonia: dry cough
- Fatigue, loss of appetite
- Fever, sweating, chills
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea
- Shortness of breath
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
- Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lung
- Tuberculosis may involve multiple organs, such as the lung, liver, spleen, kidney, brain, and bone
- but may spread to other organs
- caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. (or Tubercle bacillus)
- Formation of granuloma in infected lung
- Cell mediated hypersensitivity – Inflammation
- Fibro cavity causing destruction in lung
Stages of Tuberculous infection
Primary stage:
- exhibit symptoms 1 to 2 weeks after entry of micro-organism.
Latent stage:
- bacteria engulfed by macrophages lives in dormant phase. No symptoms. No spread of infection.
Active stage:
- whenever immune system weakens, germs will multiply and make sick.
Causes and risk factors of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Close contact with infected person
- Immunocompromised
- Substance abuse
- Pre-existing medical condition
- Immigration from high prevalence country
- Living in over crowded house
- Inadequate health care
- Malnutrition
- Health care workers
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Sign and symptoms of Tuberculosis
- Cough (dry/mucopurulent/blood) more than 3 weeks
- Fever/chills/night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Breathing difficulty
- Pain in chest
- Fluid around lung
- Enlarged/tender lymph nodes
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Signs
- Lymph nodes: swollen and tender lymph nodes
- Abdomen: pain, indigestion, diarrhoea, loss of appetite
- Bones: swelling and pain in bones
- Heart: inflammation of heart layers, chest pain
- Kidney: pain, inflammation of kidney and dysuria
- Brain: tb meningitis, behaviour changes, meningitis causing headache, drowsy, convulsion
- Skin: lumpy rashes, ulcers
Lung Carcinoma
- is a malignant lung tumor, bronchogenic Carcinoma
- tumors originating in the lung parenchyma or within the bronchi.
- characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lungs.
- If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body.
- is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths.
Epidemiology
- Lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, accounting for approximately 12.4% of all cancers diagnosed worldwide, and is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths.
- The American Cancer Society estimates an annual incidence of more than 234,000 new lung cancer cases and over 154,000 lung cancer-associated deaths in the United States.
- According to the Global Cancer Statistics report from 2020, lung cancer remained the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, with an estimated 1.8 million deaths.
- In Nepal the country profile 2018 shows lung cancer to have highest incidence and mortality.
Risk factors of Lung Cancer
- Tobacco, smoking
- Secondhand smokers
- Heredity
- Occupational and environmental exposure
- Asbestos, radon ,arsenic, mustard gas, coke oven fumes, nickle, chromates, beryllium,silica Air pollution
- Talc and talcum powder
- Radioisotope exposure, ionizing radiation
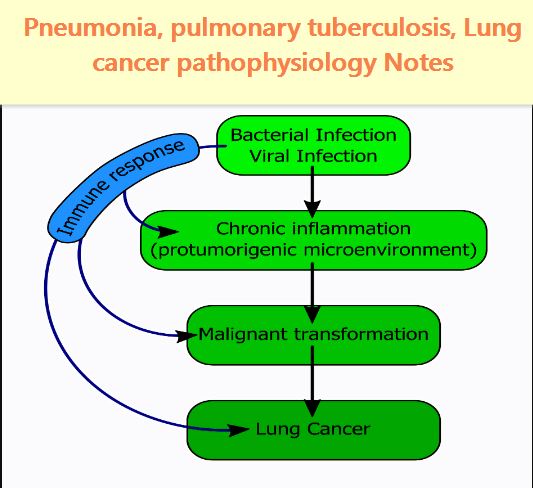
Pathophysiology of lungs cancer
TYPES OF LUNG CANCER:-
Non- small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Most common type
- About 80-85% are NSCLC
- grows more slowly
- It is further classified into the following
a. Epidermoid carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma
- 25-30% of lung cancer and more common in males
- More centrally located and arise from bronchial epithelium
- Cavitation may also occur
- Slow growth, metastasis not common
b. Adenocarcinoma
- Most prevalent carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma, arising from the bronchial mucosal glands, is the most common NSCLC cancer, representing 35-40% of all lung cancers.
- It is the subtype observed most commonly in persons who do not smoke.
- It usually occurs in a peripheral location within the lung.
c. Large cell carcinoma
- 10-15% of lung cancer
- Large abnormal looking cell
- Cavitation common
- Slow, metastasis may occur to kidney, liver and adrenals
- Metastasis via lymphatics and blood
- May be located centrally, mid lung or peripherally
2. Small cell carcinoma
- Spreads more quickly and aggressively
- 65-75%
- Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) arises in peribronchial locations and infiltrates the bronchial submucosa.
Clinical manifestations
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Bone pain
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Neurologic dysfunction