Pathology
- Latin word- ‘Pathos’ meaning suffering
- ‘Logos’ meaning study
- Study of changes of body tissues or organs which causes caused by disease
Types of Pathology
- Anatomical pathology- study of organs or tissue to diagnose a disease
- Clinical pathology- diagnosis of disease based on the lab analysis of body fluids, such as blood, urine, and so on
- Molecular pathology- biochemical and genetic approach to the study of disease on a molecular level.
Pathophysiology
- Physiology of disordered functions
- Disordered physiological processes associated with disease or injury
Pathogenesis
Progressive development (sequence of events) of a disease from the time it is initiated to its conclusion in the recovery or death process
Etiology/Aetiology
Refers to a study of the cause of a disease
- Intrinsic factor- genetic/hereditary
- Environmental factor-pathogen
Prognosis
Refers to the probable outcome of a disease in a living individual
estimate of the severity and possible result of a disease
Diagnosis
- Refers to the determination of the nature of a disease expressed in a concise manner
- Example pneumonia, Tuberculosis, meningitis
Acute
- Characterized by a sudden onset or rapid course
- Within a short clinical course
- Example flu, tonsillitis, COPD
Chronic
- Onset long duration
- have a prolonged duration
- Example
- Asthma, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, Heart disease
Idiopathic
- Disease with unknown cause
- Any disease that is of uncertain or unknown origin
- Example àacute idiopathic polyneuritis, Rheumatic Arthritis
The course of a disease
- Known as natural history
- Refers to the development of the disease in a patient including the sequence and speed of the stages and forms they take
Signs and symptoms
Symptom
- is a subjective that is reported by the patient
- Discussed in Medical History
- exampleàfatigue, cough, chest pain
Signs
- is there any objective evidence of a disease
- observed by others ( doctors, nurses,
- Discussed in Physical Exam
- Examples of skin rash , cyanosis, clubbing, wheezes
Syndrome
a group of symptoms that consistently occur together or a condition characterized by a set of associated symptoms.
Examples àDown syndrome, Compartment syndrome
Infectious
- Caused by the entrance of infectious agents into the body of organisms which grow and multiply there
- able to be passed from one person, animal, or plant to another
Bruise
- Also known as contusion- blood below the skin
- due to traumatic injury to the skin or the tissues underneath the skin
- The outer skin is not cut or broken so there is no external bleeding but damage occurs in blood vessels underneath the skin causing them to rupture and leak blood.
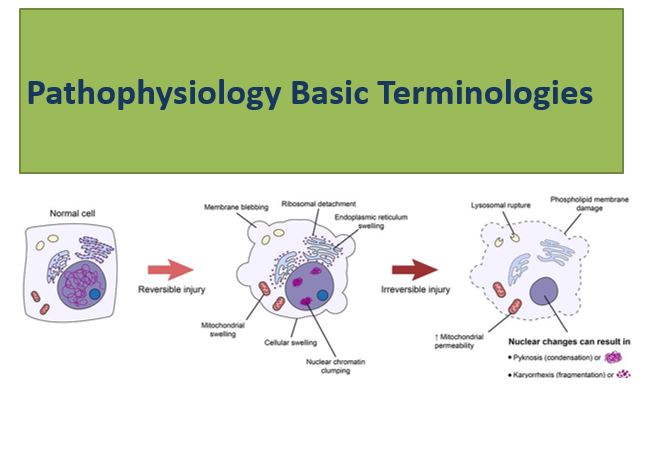
Cell Injury
- Injury to the cell and cell component due to etiological agents
- resulting in changes in its internal and external environment.
- types of Injuries to cell
- Nonlethal injury leads to reversible cell injury
- Lethal injuryà leads to irreversible cell injury and death
Cell death is followed by necrosis
Causes of cell injury
- Oxygen deprivation- hypoxia, ischemia
- Infectious agents- bacteria, virus
- Physical agents- burn, ionizing radiation
- Drugs and chemical agents- alcohol, poisons,
- Nutritional imbalance- vitamin deficiency
- Genetic defects- sickle cell anemia
- Aging
Cellular Adaptation
- When a cell is exposed to certain injurious agents, the cell may modify itself to overcome the injurious effect. This modification without any injurious effect is called cell adaptation
Types of cellular adaptation
- Atrophy
- Hypertrophy
- Hyperplasia
- Metaplasia
Atrophy
- This means the shrinkage in the cells by loss of cell or cellular structure
- Atrophic cells are not dead. They may have diminished function
- Atrophy of cells leads to atrophy of the organ
- Causes- inadequate nutrition (malnutrition), atrophy of muscle fibers, diminished blood supply
Hypertrophy
- Increase in the size of the cell and this may lead to an increase in organ
- Types:
- Physiological hypertrophy- for example, growth of the uterus (pregnancy)
- Pathological hypertrophy- for example, ventricular hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
- Increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue which may increase in volume
- It involves cell division – an increase in the number of cells
Types of Hyperplasia
- Physiological hyperplasia: female breast in puberty
- Pathological hyperplasia: thyroid gland (goiter)
Metaplasia
- Reversible adaptive change in the cell in which one adult cell is replaced by another type of cell
- Example- squamous metaplasia of the respiratory epithelium
Dysplasia
- Disordered cellular development.
- Describe a group of cells showing an abnormal pattern of growth and maturation
- Example: uterine cervix and respiratory tract, alimentary tract